TL;DR: Learn how to build a high-performance financial dashboard in Blazor using Syncfusion components. This guide covers responsive layout design, interactive charts, pivot tables for financial analysis, and proven techniques to optimize dashboard performance.
Managing financial data doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Imagine having a sleek dashboard that turns raw numbers into actionable insights, right inside your browser.
That’s where Blazor comes in. With its powerful C# based framework for building interactive client-side web UIs, it provides a solid foundation for creating rich data experiences. When combined with Syncfusion’s high-performance Blazor components, you can build enterprise-grade financial dashboards that are both powerful and intuitive.
This blog post will guide you through building a financial dashboard using Syncfusion’s Blazor Pivot Table, DataGrid, Chart, and DashboardLayout components. We’ll focus on best practices, performance optimization, and creating a visually compelling and interactive user experience.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, make sure the following components are set up:
- .NET 9 SDK: Ensure it’s installed and properly configured.
- Code Editor: Use either Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio 2022 for development.
- Syncfusion Blazor Packages: Install the necessary packages and activate them using a valid license key. If you don’t have one, you can sign up for a free 30-day trial to get started.
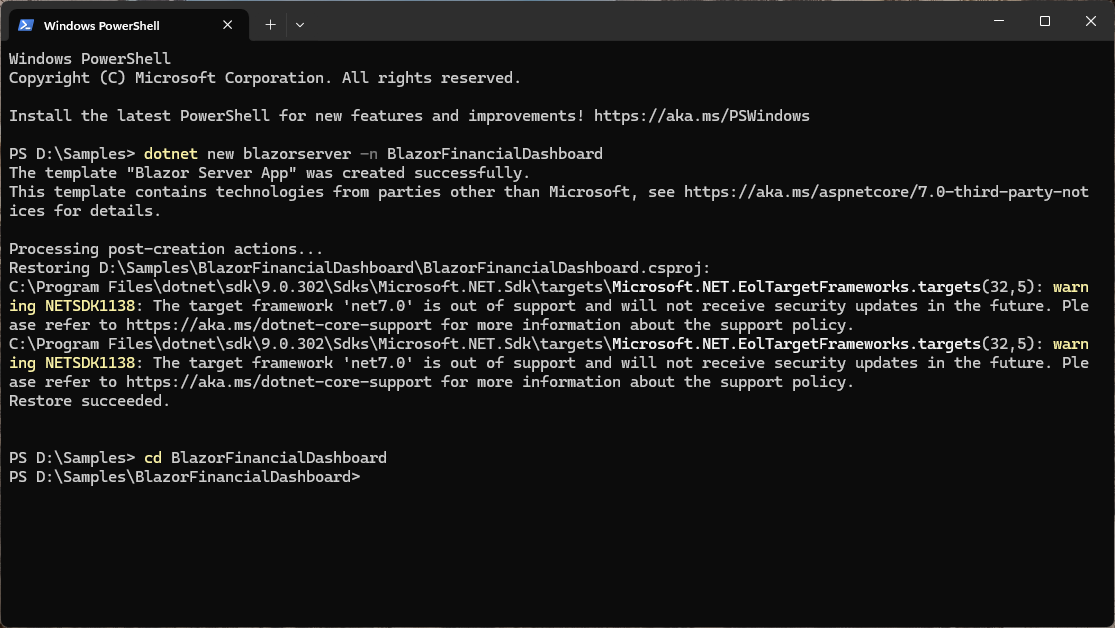
Step 1: Create a Blazor project
To begin, we’ll create a new Blazor Server application using Visual Studio Code. This sets the foundation for our financial dashboard.
dotnet new blazorserver -n BlazorFinancialDashboard
cd BlazorFinancialDashboard
Step 2: Integrating Syncfusion components
Next, we’ll add the necessary Syncfusion Blazor packages for Grid, Pivot Table, Charts, Layouts, and Themes:
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.PivotTable
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Charts
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Layouts
dotnet add package Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes
Then, register the Syncfusion services in the Program.cs.
// Program.cs
using Syncfusion.Blazor;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
…
builder.Services.AddSyncfusionBlazor(); // Register Syncfusion services
var app = builder.Build();
// ...
Next, add the Syncfusion theme and script references in _Host.cshtml. Since this demo uses only PivotTable, DataGrid, Chart, and DashboardLayout, include their specific scripts to optimize performance and reduce load time, as shown in the example below.
// Pages/_Host.cshtml
<head>
…
<link href="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Themes/bootstrap5.css" rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
…
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid/scripts/sf-grid.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.PivotTable/scripts/sf-pivotview.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Charts/scripts/sf-chart.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
<script src="_content/Syncfusion.Blazor.Layouts/scripts/sf-dashboard-layout.min.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</body>
Finally, add the Syncfusion Blazor namespaces to _Imports.razor to make the components available throughout the application.
// _Imports.razor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Grids
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.PivotView
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Charts
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.Layouts
Step 3: Build the dashboard layout
A well-structured dashboard is key to delivering an excellent user experience. The SfDashboardLayout component offers a flexible, grid-based layout that allows users to easily rearrange and resize panels.
To implement this, create a new Razor component named FinancialDashboard.razor in the Pages folder. In this layout, we’ll define three panels: one for the DataGrid, one for the Pivot Table, and one for the Chart.
@page "/financial-dashboard"
<SfDashboardLayout Columns="6" CellSpacing="new double[] { 10, 10 }">
<DashboardLayoutPanels>
<DashboardLayoutPanel Id="gridPanel" Row="0" Column="0" SizeX="6" SizeY="2">
<HeaderTemplate><h3>Transaction Details</h3></HeaderTemplate>
<ContentTemplate>
@* DataGrid will go here *@
</ContentTemplate>
</DashboardLayoutPanel>
<DashboardLayoutPanel Id="pivotPanel" Row="2" Column="0" SizeX="3" SizeY="4">
<HeaderTemplate><h3>Financial Analysis</h3></HeaderTemplate>
<ContentTemplate>
@* Pivot Table will go here *@
</ContentTemplate>
</DashboardLayoutPanel>
<DashboardLayoutPanel Id="chartPanel" Row="2" Column="3" SizeX="3" SizeY="4">
<HeaderTemplate><h3>Income vs. Expense</h3></HeaderTemplate>
<ContentTemplate>
@* Chart will go here *@
</ContentTemplate>
</DashboardLayoutPanel>
</DashboardLayoutPanels>
</SfDashboardLayout>
Step 4: Display detailed data with DataGrid
The SfGrid component is perfect for displaying and managing tabular data. In this dashboard, we’ll use it to present a list of financial transactions in a clean, interactive format.
First, create a model to represent your financial data.
// Models/FinancialData.cs
public class FinancialData
{
public int TransactionID { get; set; }
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal Amount { get; set; }
public string Type { get; set; } // "Income" or "Expense"
}Then, add the SfGrid to our FinancialDashboard.razor component to bind and display the data.
// Inside the gridPanel ContentTemplate in FinancialDashboard.razor
<SfGrid DataSource="@transactions" AllowPaging="true" AllowSorting="true" Height="100%">
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.TransactionID)" HeaderText="ID" Width="80"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.Date)" HeaderText="Date" Format="d" Width="120"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.Description)" HeaderText="Description"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.Category)" HeaderText="Category" Width="150"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.Amount)" HeaderText="Amount" Format="C2" Width="120"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field="@nameof(FinancialData.Type)" HeaderText="Type" Width="100"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
@code {
private List<FinancialData> transactions = new();
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
// Populate with sample data
transactions = GetFinancialData();
}
private List<FinancialData> GetFinancialData()
{
// ... implementation to get data
return new List<FinancialData>(); // return sample data
}
}Step 5: Analyze data with Pivot Table
The SfPivotView component is the centerpiece of our financial dashboard, enabling powerful multi-dimensional analysis.
Add SfPivotView to the FinancialDashboard.razor component and configure it to display total amounts by category and type, with drill-down capability by year. This setup gives users a clear, interactive view of financial trends.
// Inside the pivotPanel ContentTemplate in FinancialDashboard.razor
<SfPivotView TValue="FinancialData" DataSource="@transactions" Height="100%" Width="100%">
<PivotViewDataSourceSettings DataSource="@transactions" ExpandAll="false">
<PivotViewColumns>
<PivotViewColumn Name="Year"></PivotViewColumn>
</PivotViewColumns>
<PivotViewRows>
<PivotViewRow Name="Category"></PivotViewRow>
<PivotViewRow Name="Type"></PivotViewRow>
</PivotViewRows>
<PivotViewValues>
<PivotViewValue Name="Amount" Caption="Total Amount"></PivotViewValue>
</PivotViewValues>
</PivotViewDataSourceSettings>
</SfPivotView>
@code {
// ... existing code ...
public class FinancialData
{
// ... properties
public string Year => Date.Year.ToString();
}
}Step 6: Visualize trends with charts
The SfChart component makes it easy to turn raw data into meaningful visuals. For this dashboard, we’ll create a Column Chart to compare income vs expenses, providing users with a quick snapshot of financial trends.
// Inside the chartPanel ContentTemplate in FinancialDashboard.razor
<SfChart DataSource="@chartData" Height="100%" Width="100%">
<ChartPrimaryXAxis ValueType="Syncfusion.Blazor.Charts.ValueType.Category"></ChartPrimaryXAxis>
<ChartSeriesCollection>
<ChartSeries DataSource="@chartData" XName="Category" YName="Amount" Type="ChartSeriesType.Column"></ChartSeries>
</ChartSeriesCollection>
</SfChart>
@code {
// ... existing code ...
private List<ChartData> chartData = new();
protected override void OnInitialized()
{
transactions = GetFinancialData();
chartData = transactions
.GroupBy(t => t.Category)
.Select(g => new ChartData { Category = g.Key, Amount = g.Sum(t => t.Amount) })
.ToList();
}
public class ChartData
{
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal Amount { get; set; }
}
}Step 7: Optimize performance
Handling large datasets efficiently is critical for a smooth user experience. Syncfusion Blazor components are built with performance in mind, and here are some best practices to make your dashboard lightning-fast:
- Virtualization: Both SfGrid and SfPivotView support virtualization to render large datasets without slowing down the UI. Enable it by setting EnableVirtualization to true.
- On-demand loading: For the Pivot Table, you can set AllowDeferLayoutUpdate to true. This prevents unnecessary re-rendering during UI interactions.
- Server-side data processing: For massive datasets, you can process data on the server and send only the aggregated data to the client. This reduces payload size and improves responsiveness.
The output of the application will appear as shown in the following GIF.
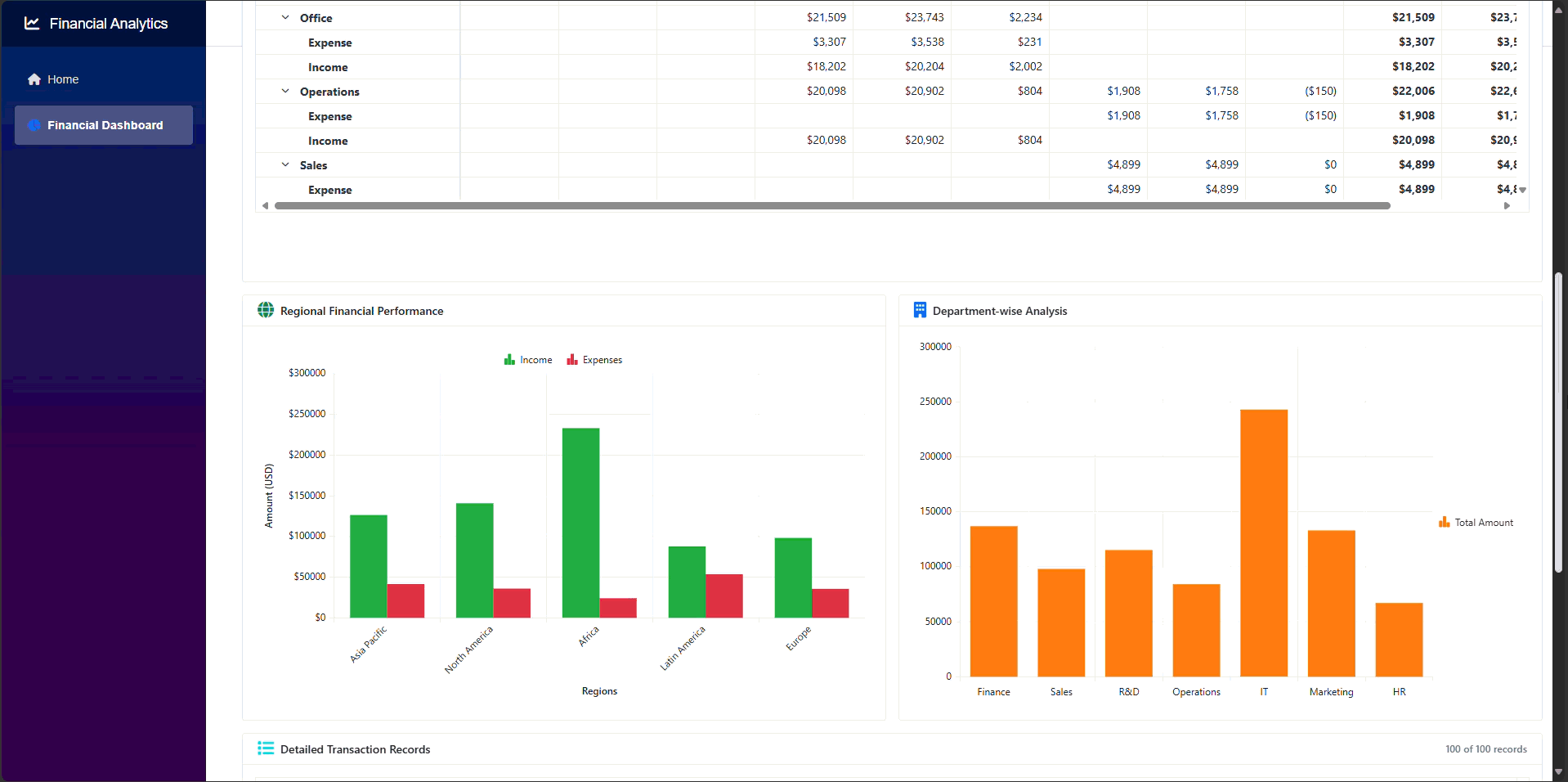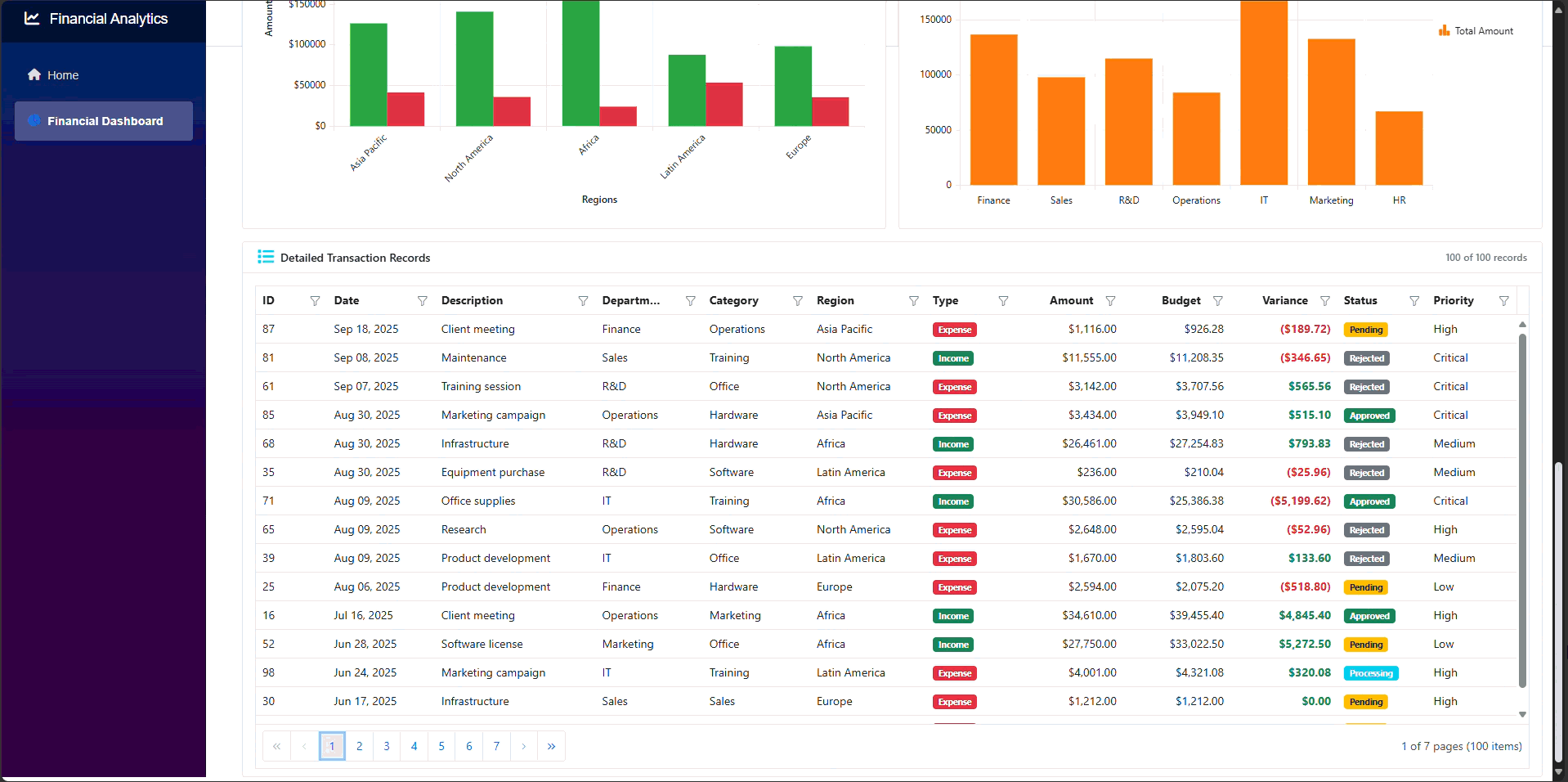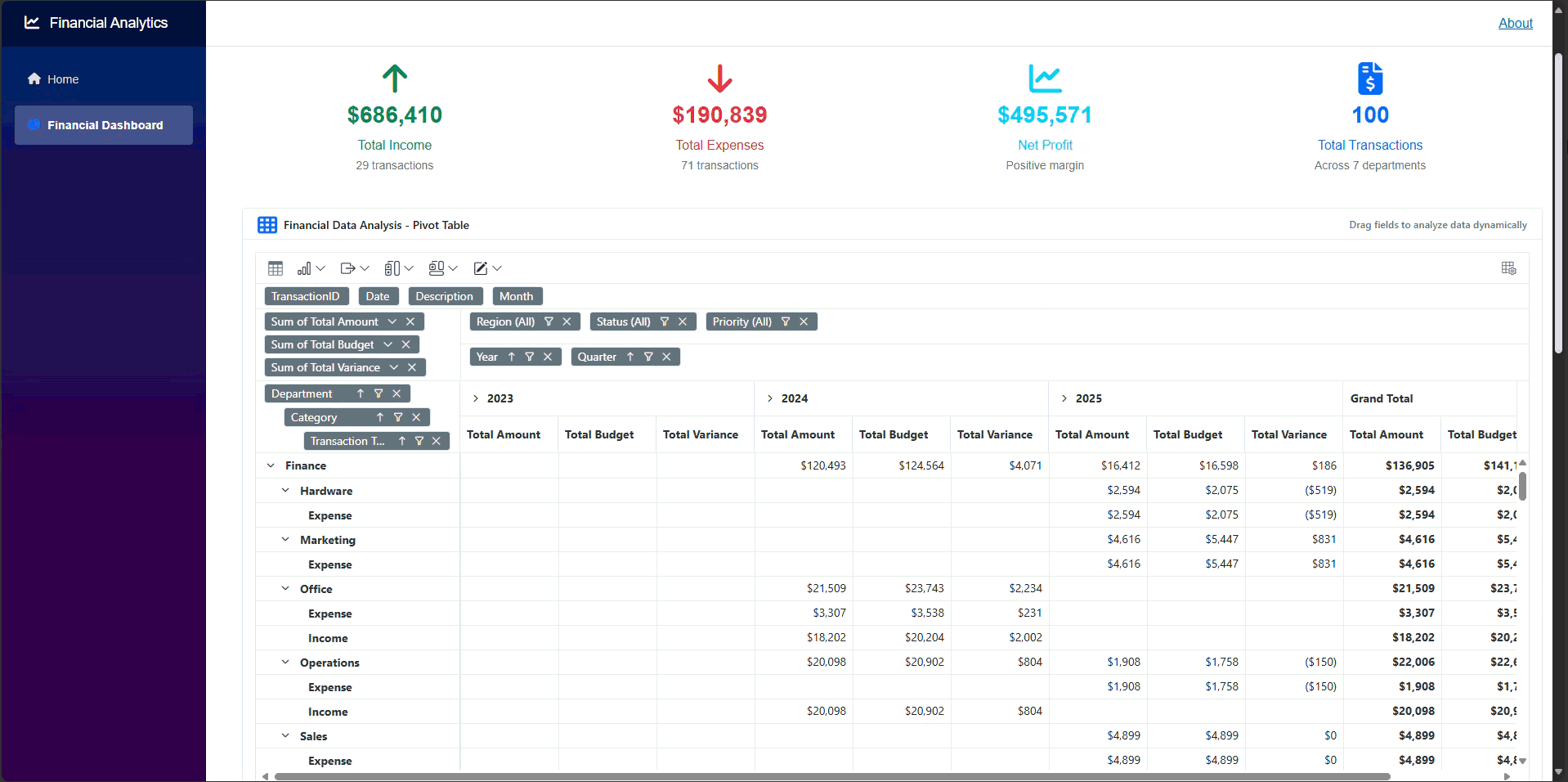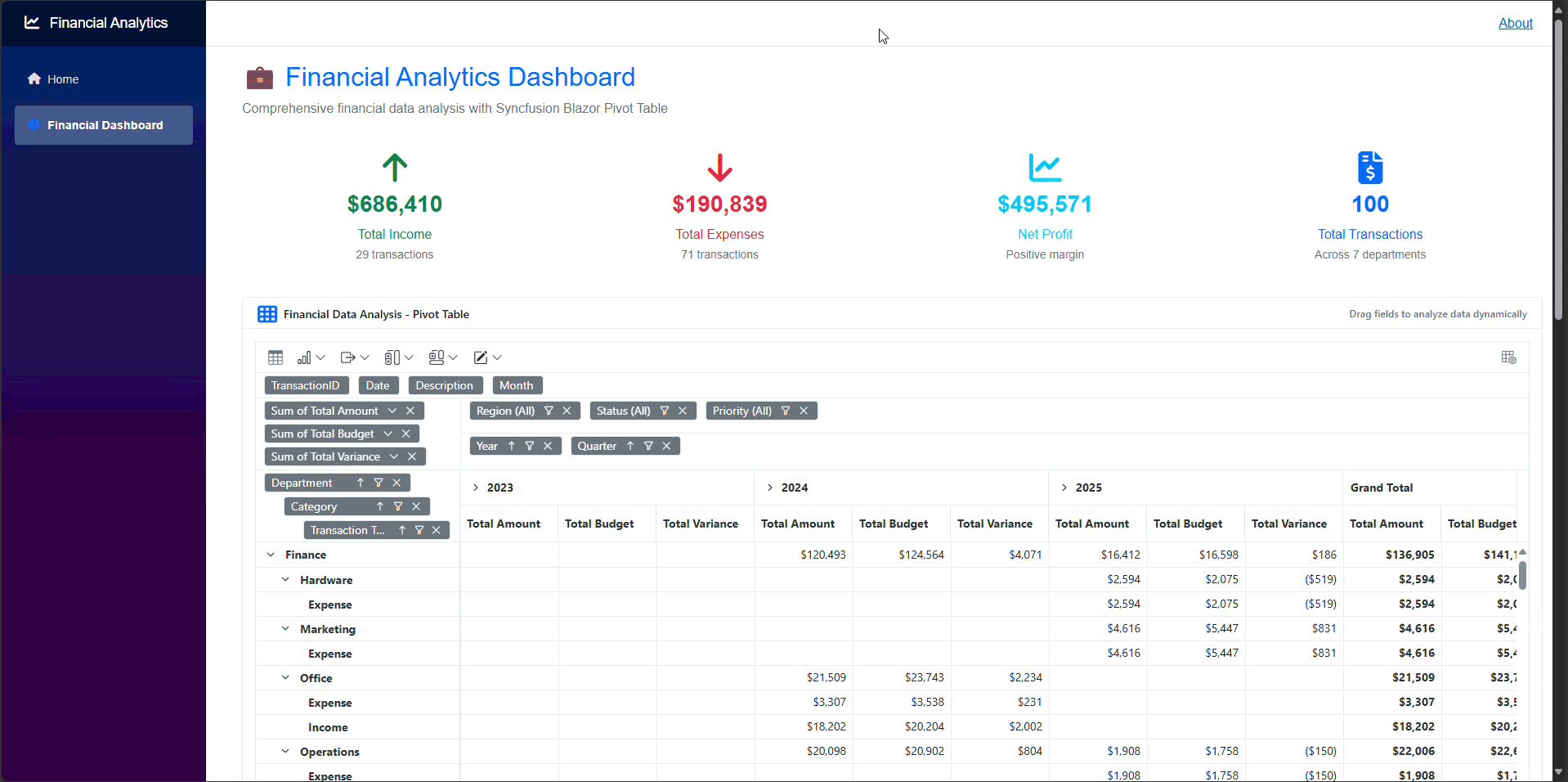
GitHub reference
For more details, you can view the complete source code for this example on GitHub.

Syncfusion Blazor components can be transformed into stunning and efficient web apps.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading! In this guide, we demonstrated how to build a financial dashboard using Syncfusion Blazor components. We utilized SfDashboardLayout to create flexible layouts, displayed transaction data with SfGrid, performed multi-dimensional analysis using SfPivotView, and visualized trends through SfChart.
By combining Blazor’s flexibility with Syncfusion’s high-performance components, you can create dashboards that deliver real-time insights and an exceptional user experience. To learn more about Syncfusion Blazor components, check out the official documentation.
If you’re a Syncfusion user, you can download the setup from the license and downloads page. Otherwise, you can download a free 30-day trial.
You can also contact us through our support forum, support portal, or feedback portal for queries. We are always happy to assist you!