CHAPTER 6
Security
Another important management task is implementation of security. You must add users to the SQL Reporting server and assign each user to a role. Then you map roles for report items, either at the folder level or the item level, to control what each user can see and do.
Role-Based Security
Before allowing users to access the SQL Reporting server, you should have a clear understanding of the role-based security model that SQL Reporting uses to authorize user activity on the server. There are two types of roles on the server:
- Item
- System
Item Roles
You use item roles to define permissions granting access to folders, reports, and other resources uploaded to the server such as images, shared datasets, report parts, and data sources. If you secure a folder, any content contained in that folder automatically has the same permissions. However, you can override inherited security and secure individual items by assigning different permissions.
SQL Reporting includes the following item roles:
- Content Manager. This role has permissions to see an item and to perform management tasks related to the item. This role can add an item to the SQL Reporting server and can configure security if the user is also a co-administrator of the subscription. Typically you set up a limited number of Content Managers on the server.
- Publisher. This role has permissions to see an item and add an item. However, the role does not have permissions to configure security. You usually assign this role to report developers.
- Report Builder. This role allows a user to open a report on the SQL Reporting server in Report Builder to edit the report.
- My Reports. With this role on an on-premises server, a user has permissions to save reports to a personal folder on the report server. However, the My Reports feature is not available in SQL Reporting at the time of this writing.
- Browser. Most report readers are assigned to the Browser role. This role can only view an item.
Note: To add a co-administrator to a subscription, go to the Settings page of the Windows Azure management portal, click the Administrators link at the top of the page, click Add on the ribbon at the bottom of the page, type the email address of the new administrator, and select a subscription
System Roles
You use system role assignments to enable users to perform administrative tasks on the report server. You assign each user to one of the following roles:
- System Administrator. A user assigned to this role can connect to the SQL Reporting management portal to perform administrative tasks. The user can also connect to the SQL Reporting server in SSMS to view and update server properties.
- System User. Most users are assigned to this role. Users in this role cannot connect to the SQL Reporting management portal.
Users
After the SQL Reporting server is set up, only the server administrator has permissions to access the server’s management portal and to deploy reports. Report readers initially have no access. You must create a user account for each report reader to grant access to the server and assign the user to item and system roles.
In the management portal, click Manage and then, in the Manage Users dialog box, click Create User. Type a name and password, and then select the applicable roles. Typically, you assign report readers to the Browser item role and the System User system role as shown in Figure 49. The item role assignment is the default role for the user, which you can override for individual items on the SQL Reporting server.
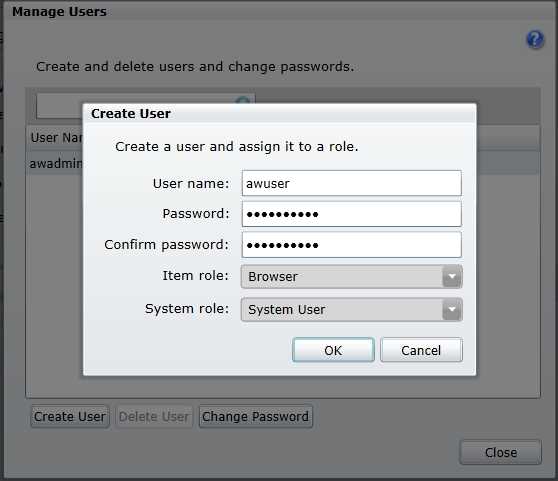
- User role assignments
Report Server Item Permissions
The item role assignments for users automatically apply to each item on the SQL Reporting server. That is, a user assigned to the Browser role can view all folders and the contents of each folder. However, you can override these role assignments at the folder level or item level. To do this, click the arrow next to the item you want to secure in the SQL Reporting management folder, and select Permissions.
By default, the Inherit Permissions From Parent check box is selected, as shown in Figure 50. In the Manage Permissions dialog box, you can see the list of users already assigned to a role for the current item and the role assignment. To override the role assignment, clear the Inherit Permissions From Parent check box if necessary, select a user, and then select the new role’s check box.

- Report item permissions
You can assign users to different roles for different content on the SQL Reporting server. For example, you might have all users assigned to the Browser role on the top-level folder. Then you can assign the users in the sales department and the finance department to the Browser role for the folders for their respective departments. Then for each folder, you can assign different users to the Content Manager role. For example, as shown in Figure 51, you can designate John as the content manager of the top-level folder, Amy as the content manager of the Sales folder, and Linda as the content manager of the Finance folder.

- Report items and role assignments
Note: Any user assigned to the Content Manager role for a data source (or its parent folder if it inherits security) can view the connection string it contains and the user account used to connect to the SQL Database. However, the password is not visible. Nonetheless, you should keep this information secure. Review permissions for each data source and limit the Content Manager role assignment to as few people as possible.

- 1800+ high-performance UI components.
- Includes popular controls such as Grid, Chart, Scheduler, and more.
- 24x5 unlimited support by developers.

