CHAPTER 9
Visual Studio 2015 for Mobile Development
The latest releases of Visual Studio provided optimal support for building mobile applications on top of Microsoft operating systems and platforms, such as Windows Phone 7.x, Windows Phone 8.x, and Windows 8.x. However, these IDEs only support app development for devices running Microsoft operating systems. It’s no secret that a huge role in the market of mobile devices, such as tablets and smartphones, is played by Android and iOS operating systems. Microsoft is aware of this and with Visual Studio 2015 they open up to new scenarios, providing tools for building cross-platform mobile apps. This chapter provides you with a background about what possibilities you have in Visual Studio 2015 and explains new opportunities for different platforms.
The Background
One of the biggest goals for developers working on mobile apps is the ability to write an app once and see it run on multiple devices and operating systems. This is actually the meaning of cross-platform mobile development. Without a doubt, Microsoft Visual Studio has been the best development environment for many years. The IDE supports many languages (including HTML5 and JavaScript, the most popular language for building cross-platform apps), offers rich designers for every supported development platform, interactive code editors, debugger integration, code analysis, and productivity features. It also simplifies how developers manage the application development lifecycle with powerful visual tools and services. Before Visual Studio 2015, only developers building apps for Windows Phone and Windows 8.x could take advantage of such a rich development environment. The only exception is Visual Studio 2013, which allows cross-platform development with a third-party product by Xamarin. Visual Studio 2015 and the new .NET ecosystem mark a revolutionary time for Microsoft: the company is open-sourcing many building blocks of the .NET runtime. Similarly, Visual Studio 2015 now allows building cross-platform mobile applications using non-.NET platforms and libraries to target Android and iOS operating systems. This means that Microsoft is trying to attract developers who have been using less-evolved environments like Eclipse and Cocoa/Objective C; developers can finally use Visual Studio to leverage all of its power and productivity tools.
What Mobile Apps Can I Build with VS 2015?
Visual Studio 2015 is the most complete development environment for building mobile apps. With this release, you can build:
- Apps for Windows 10. At the time of publication, Windows 10 is available as a Technical Preview and you can build apps for the pre-release version by installing the developer tools for Visual Studio 2015.
- Apps for Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 using XAML and C#/VB.
- Apps for Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1 using XAML and C#/VB.
- Universal Windows Apps using XAML and C#. Visual Basic is also supported but requires some additional, manual steps.
- Apps for Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 using WinJS libraries (HTML5/JavaScript).
- Apps for Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1 using WinJS libraries (HTML5/JavaScript).
- Universal Windows Apps using WinJS libraries (HTML5/JavaScript).
- Cross-platform apps for Windows, Windows Phone, Android, and iOS with C#/F# and XAML installing extensions and tools from Xamarin.
- Cross-platform apps for Windows, Windows Phone, Android 2.3.3 and later, and iOS (6, 7, and 8) using Apache Cordova and the integrated Visual Studio Tools for Apache Cordova.
Note: Windows 10 app development is not covered in this book because the Universal Windows Platform application model is a very complex environment; there are also several ways to develop Universal apps, including porting existing iOS and Android code, which would cover an entire book
Microsoft and Xamarin joined together in a partnership to make better tooling integration in Visual Studio 2015. However, the Xamarin suite does not ship with Visual Studio and is a product that you must purchase separately. For building apps for Windows 8.x and Windows Phone 8.x with either XAML/.NET or HTML5/JavaScript, the MSDN library provides very good documentation. That said, in this chapter we focus on new tools for building apps using the JavaScript APIs from Apache Cordova with Visual Studio 2015, including a brand new Android emulator built by Microsoft.
Note: From now on, I will refer to Apache Cordova with either its full name or simply with Cordova.
Prerequisites
To develop cross-platform mobile apps with Visual Studio 2015 and Apache Cordova, you need to install some prerequisites. These are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3—Apache Cordova Prerequisites
Prerequisite | Description |
|---|---|
Apache Ripple | Emulator for Android and iOS. |
Google Chrome | Web browser and components required to run the Ripple emulator. |
Apache Ant 1.8.0 | Required for the Android build process. |
Android SDK | Required for the Android build process and for the Ripple emulator. |
Oracle Java SDK 7 | Required for the Android build process. |
Node.js | Integrates Visual Studio with the Apache Cordova Command Line Interface (CLI) and the Ripple emulator. |
Apple iTunes | Required to remotely deploy an app to an iOS device. |
The Visual Studio 2015 installer will install all of the prerequisites for you, just be sure you select all the required components in the installer’s welcome window.
Note: Hyper-V is another prerequisite, as it is required to run the Visual Studio Emulator for Android and emulators for Windows Phone 8.1.
Building Apps for iOS
iOS apps cannot be built on Windows. This is not a Windows limitation; it is instead the Apple license that requires developers to build apps on a Mac. For this reason, in order to use Visual Studio 2015 and Apache Cordova to build apps for iOS, you need a Mac computer and some additional configuration for remote debugging. The MSDN documentation has a specific document about configuring an environment with iOS. In this book, we do not cover iOS development because we cannot assume readers have a Mac and because we focus on tools that you can use on Windows and Visual Studio. In this chapter, we talk about Android development with Visual Studio 2015.
Building Apps with Apache Cordova
Apache Cordova is an open-source project that provides a rich set of APIs that enable developers to access native device functions from JavaScript code. For instance, with these APIs you can easily access the device’s camera or other sensors. When using Apache Cordova, you basically use JavaScript and do not write a single line of native languages like Java, Objective-C (iOS), or C#. Cordova’s JavaScript APIs only allow accessing device capabilities, so you need a combination with a UI framework such as jQuery Mobile or Dojo Mobile. The combination of Cordova and a UI framework allows for writing mobile apps with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Both Cordova’s JavaScript APIs and UI frameworks are consistent across multiple device platforms, so an app that you build with Cordova can run on multiple operating systems and devices. This is where Microsoft Visual Studio 2015 comes in. The IDE integrates the usual, powerful visual environment with all of its tools with Apache Cordova to provide the best development experience for cross-platform mobile applications, and makes it easy to integrate Cordova projects with UI frameworks. After all, Visual Studio has had enhanced support for JavaScript for many years, with continuous improvements made to the code editor. Of course, we assume that you know how to code in JavaScript to take advantage of the features described in this chapter.
Visual Studio Tools for Apache Cordova
Behind the scenes, Visual Studio 2015 is able to support development with Cordova via Visual Studio Tools for Apache Cordova, an extension that is part of the IDE. Among others, these tools offer a project template called Blank App (Apache Cordova), which is located in the Apache Cordova Apps node under the JavaScript folder, in the New Project dialog (see Figure 94).
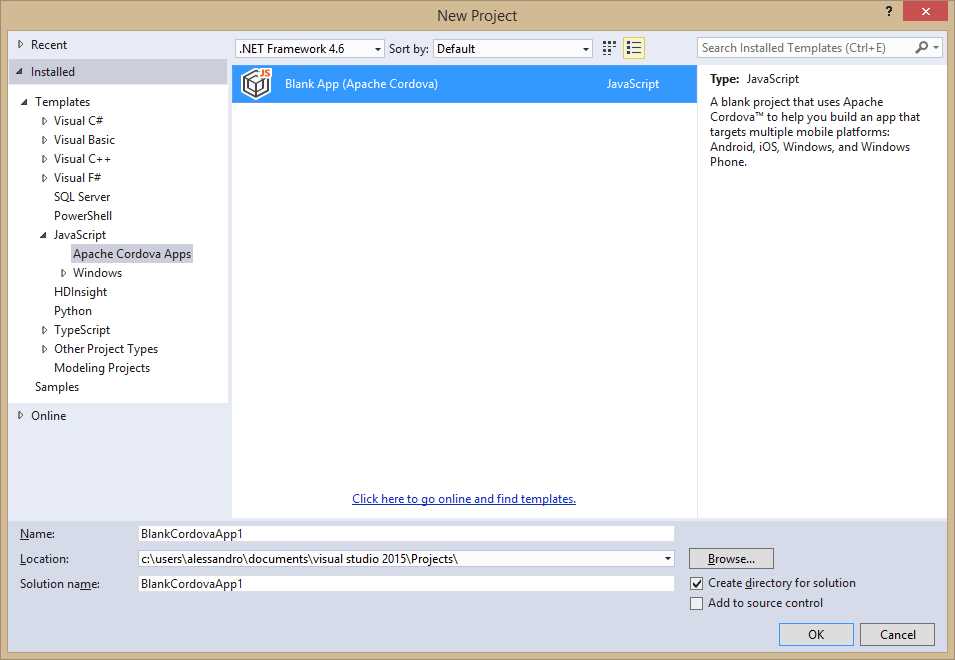
- The Apache Cordova project template.
When you create a Cordova project, Visual Studio shows a “Getting started” page with many useful links; you will see many common elements in the Solution Explorer (see Figure 95) like:
- An index.html file, which is the home screen for your app.
- A config.xml file, which contains configuration information and that can be edited with a visual editor simply double-clicking it.
- Platform-specific folders containing optimized icons, resources, and scripts for Android, iOS, and Windows/Windows Phone.
- A res folder, which contains platform-specific JavaScript code. It is organized in subfolders, each targeting a specific platform.
- A script folder, the default location for JavaScript or TypeScript files.
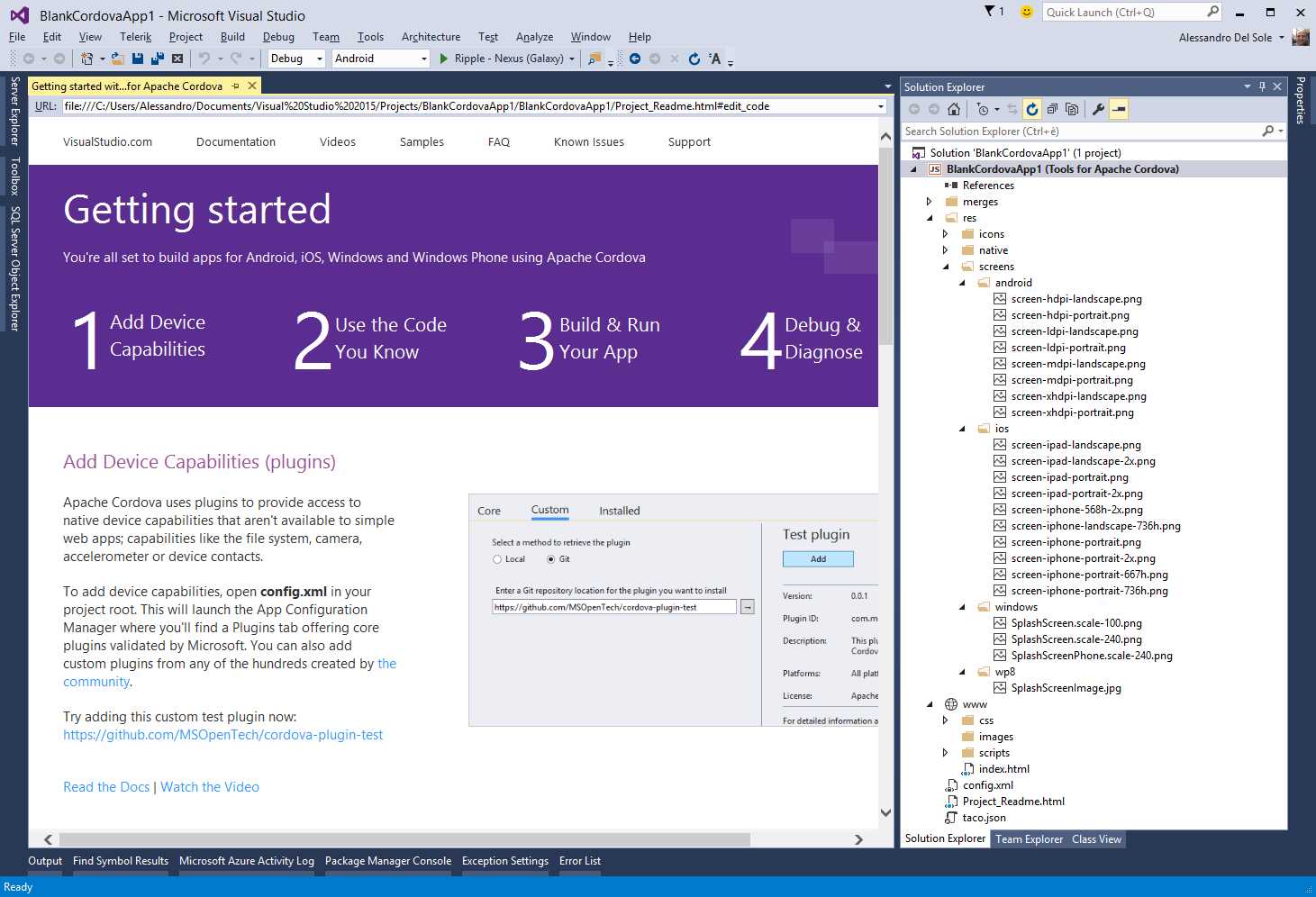
- The Apache Cordova project structure.
Configure the project by double-clicking the config.xml file. When you do this, Visual Studio 2015 shows a special designer, which is shown in Figure 96.
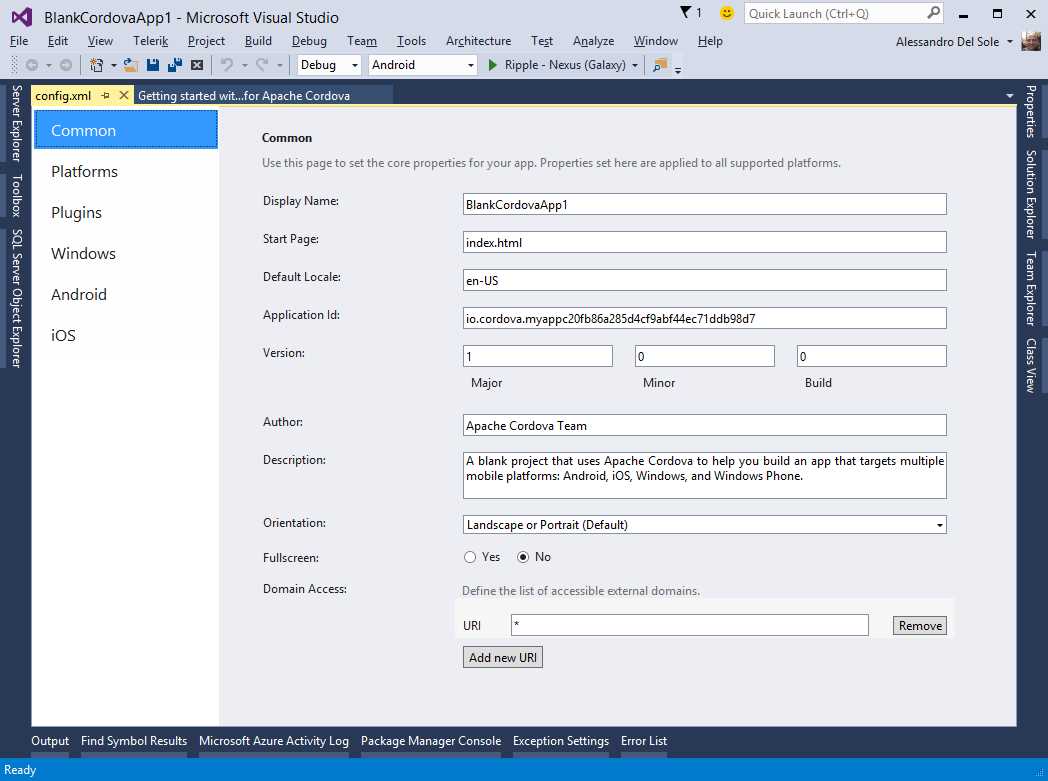
- Configuring common app properties.
The configuration designer is made of six tabs. The Common tab is about common properties, which are all self-explanatory. The Platform tab allows you to specify the version for the Cordova CLI (Command-Line Interface), the infrastructure required to build and test Cordova apps. The Plugins tab (see Figure 97) is very important because it allows you to add plugins; each plugin provides an API to access specific device features.
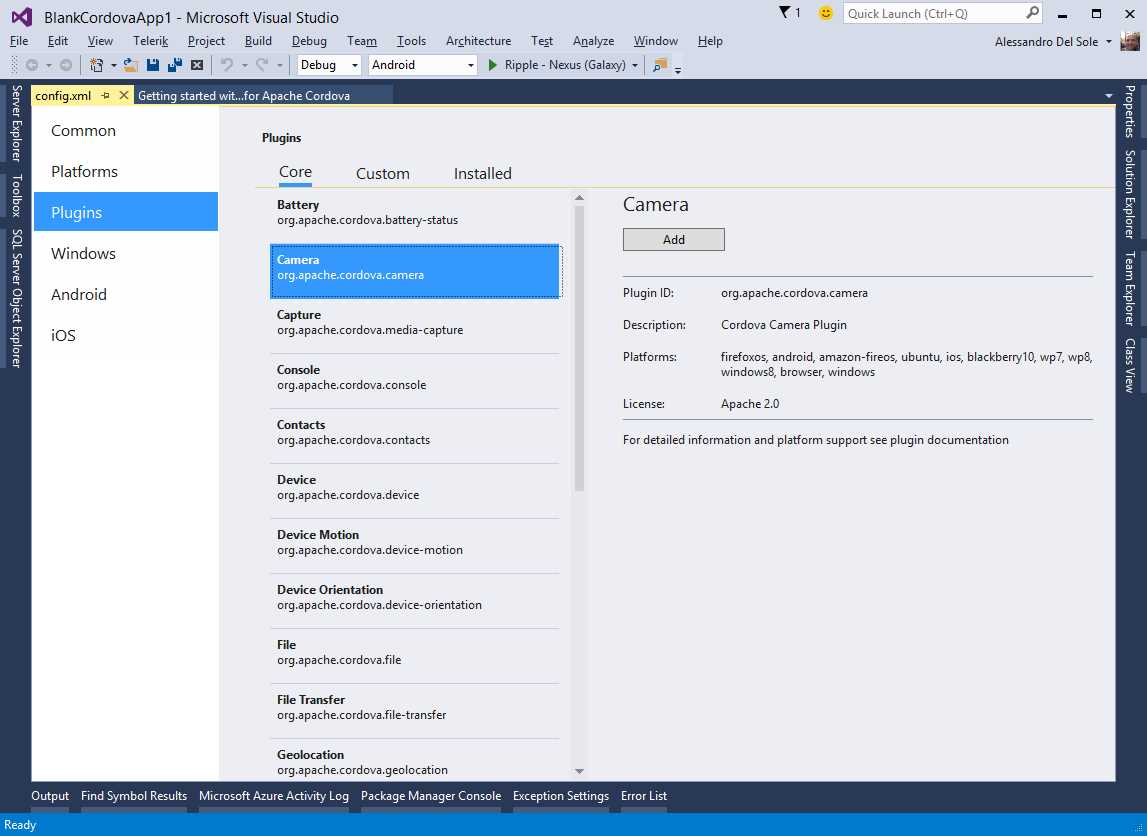
- Adding device access functionalities with plugins.
It is worth mentioning that, for every plugin, Visual Studio 2015 shows the supported platforms. When you add a plugin, Visual Studio adds to the project a number of JavaScript files and platform-specific files that you can easily discover in Solution Explorer. The other tabs allow setting platform-specific options, especially information for app stores. Exploring those tabs is left to you as an exercise. To understand how testing apps works, a good idea is to use one of the existing examples for Apache Cordova.
Note: Using an existing example is also a good idea because this book doesn’t explain plugins or detail all the Cordova APIs.
The MSDN documentation offers a sample app called ToDoList. This example is available in three different flavors, each using a different UI framework. For the current example, download the AngularJS version and extract the downloaded .zip archive to a local folder on your hard drive. The ToDoList app is very nice because it is also an example of how to use Bing Maps and connected services. Assuming you have opened the sample solution in Visual Studio 2015, at this point you want to try the sample app. Select the target operating system, which can be done via the appropriate combo box on the standard toolbar, as shown in Figure 98.
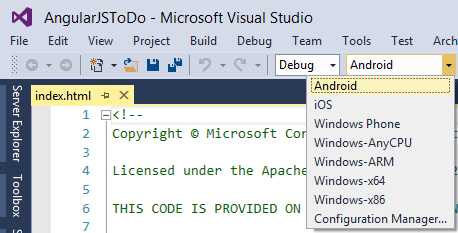
- Specifying the target operating system.
Next, you have to select where you want to run your app, which can be a physical device or an emulator, as shown in Figure 99.
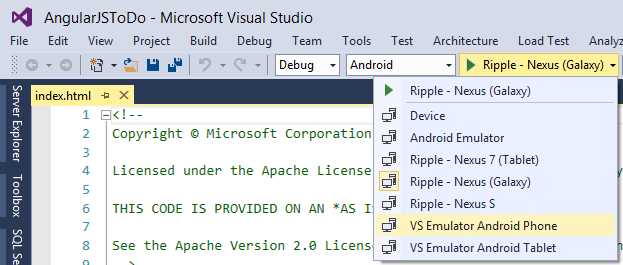
- Selecting a physical device or an emulator.
You have several different options, especially for Android. You have the Android Emulator, which is included in the Android SDK, as well as the Ripple emulator, which ships with Cordova; finally, you have the new Visual Studio Emulator for Android. For the current example, select the VS Emulator Android Phone and press F5.
The Visual Studio Emulator for Android
In addition to the existing Android emulators, Microsoft has developed a new Visual Studio Emulator for Android. Figure 100 shows the sample app running inside this new emulator.
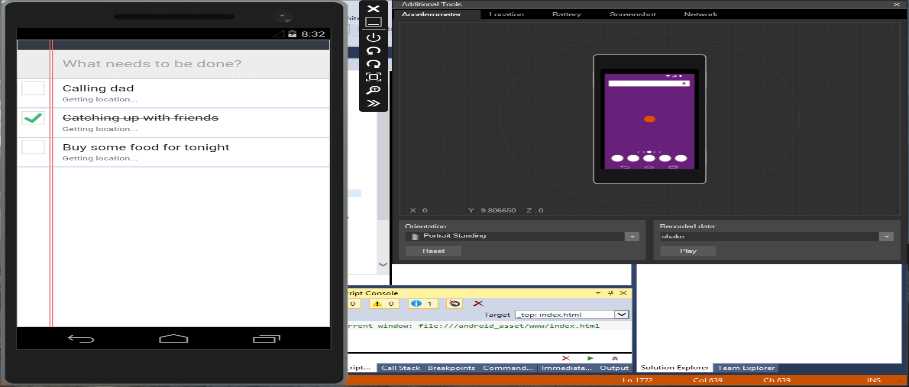
- The Visual Studio Emulator for Android.
If you have built apps for Windows Phone, the Android emulator will look familiar as they have similar layouts and tools; both include the ability to simulate sensors like the accelerometer and location, or to take screenshots. This emulator also offers an important feature for testing, which is adjusting the battery level. The emulator also has support for camera, simulating an SD card, audio playback, and keyboard input. On the Visual Studio Blog you can find a detailed blog post about available features in the Android emulator. Behind the scenes, Visual Studio creates a virtual machine hosted in Hyper-V. Additional tutorials and code examples can be found in the MSDN documentation.
Packaging and Deploying Apache Cordova Apps
As a general rule, mobile apps must be packaged into a proper binary file and deployed to the platforms’ stores. Android, iOS, and Windows apps have different characteristics and different stores. Fortunately, Visual Studio 2015 makes it easy to create packages for all the supported platforms by editing the config.xml file via a convenient designer. When you build the solution, Visual Studio creates a subfolder called bin where you can find packages for each platform. Once you have built your project, you will need to deploy the app package to the appropriate store, as you would normally do. Additional information on building packages can be found on the specific MSDN page.
Chapter Summary
Cross-platform mobile development is a key topic when talking about Visual Studio 2015. This chapter gave you an overview of the possibilities you currently have to build mobile apps with Visual Studio. You then learned about new features for building mobile apps for Android and iOS, as well as for Windows 8.x and Windows Phone 8.x, with the Visual Studio Tools for Apache Cordova. You have project templates, the complete Visual Studio tooling, and now a brand new Visual Studio Emulator for Android, which simplifies the process of testing your apps by simulating device capabilities.

- 1800+ high-performance UI components.
- Includes popular controls such as Grid, Chart, Scheduler, and more.
- 24x5 unlimited support by developers.

