CHAPTER 1
Introduction
What is Keystone.js?
Keystone.js is a Node.js web framework for developing database-driven websites, applications, and RESTful APIs. The framework is built on Express.js and MongoDB, and follows the Model-View-Template design pattern. Express.js is the de facto web application server framework for Node.js-based applications. MongoDB is a very popular NoSQL database. Keystone.js is free and open source. The framework does a lot of heavy lifting and allows developers to focus on clean and rapid development.
Keystone.js, as with Node.js applications, emphasizes reusability and modularity of components. The framework makes it very easy to manage the application templates, views, and routes. JavaScript is used throughout for configuration, files, and data model development. The framework helps with most common web tasks out of the box, such as authentication, content administration, session management, email-sending, and many more tasks.
The framework provides an automatic administration interface that can be used to create, read, update, and delete data in the application. The administration GUI is generated dynamically through inspection of models and user options. Developers can use 20+ built-in field types that provide the capability to manage data ranging from text, dates, geolocation, and HTML to images and files uploaded to Amazon S3 or Microsoft Azure.
More information is available at the official website.
Installing Node.js
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform runtime environment that is most commonly used for developing JavaScript-based, server-side web applications. Node.js is becoming a very popular tool of choice for building highly performant and scalable web applications due to its async model of handling requests on a single thread. Node.js can be installed on a wide variety of operating systems including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS. This book will primarily focus on running Keystone.js on Node.js in a Windows environment.
To install Node.js:
- Visit the download page on the Node.js official website.
- Click on the download link for the latest stable release .MSI under Windows 32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your machine architecture.
- Once the download is complete, double-click on the installer file, which will launch the Node.js installer. Proceed through each step of the installation wizard.
Figure 1: Node installer
At the Custom Setup screen during the installation, make sure that the wizard installs NPM (Node Package Manager) and configures the PATH environment variable along with installing the Node.js runtime. This should be enabled by default for all installations.
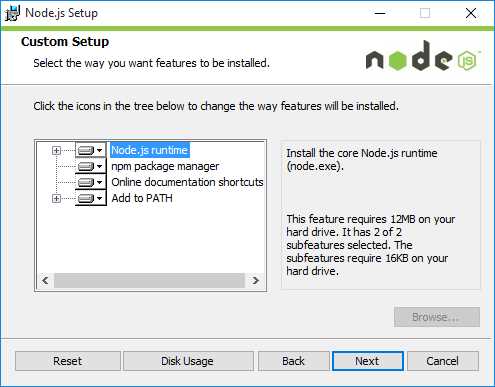
Figure 2: Custom Setup screen
Once these steps have been completed, both Node and NPM should be installed on your system.
Testing whether Node.js is installed properly
Run the following commands on a new command prompt window. You might need to open a new instance of command prompt for the PATH variable changes to take effect. We should see the versions output on the screen.

Figure 3: Node and NPM version check
Installing MongoDB
MongoDB is an open-source, document-oriented database that is designed to be both scalable and easy to work with. MongoDB stores data in JSON-like documents with dynamic schema instead of storing data in tables and rows like a relational database (such as MySQL).
Tip: MLab offers a free managed sandbox for MongoDB that can be used as a test ground instead of installing MongoDB locally.
To install MongoDB locally:
- Navigate to the MongoDB download page.
- Click on the download link for the latest zip archive or MSI under Windows 32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your machine architecture.
- Once the download is complete, extract the contents to a folder under C:\mongodb or install to program files using the MSI.
- Create the default database path (C:\data\db). This is the location where the database files used by MongoDB will reside.
- To start the MongoDB database, open a CMD prompt window, and enter the following code (you may have to allow access through a firewall).
Code Listing 1: Start MongoDB
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\3.2\bin>mongod.exe |
Figure 4: Start up the MongoDB server
Installing Yeoman
Yeoman is a set of tools for automating development workflow. It scaffolds out a new application along with writing build configuration and pulling in build tasks and NPM dependencies needed for the build. Keystone.js provides a very handy Yeoman generator to generate a new project.
To install Yeoman, issue the following command on a command prompt.
Code Listing 2: Install Yeoman
c:\> npm install -g yo |
Next, to install the Yeoman keystone app generator, use the following command.
Code Listing 3: Install Yeoman generator for keystone
c:\> npm install -g generator-keystone |
This installs the generator as a global package, and can be used to generate new projects without needing to reinstall the Keystone.js generator.
Summary
We have reached the end of the first chapter. Setting up a development environment is a very important task, and we just did this. We’ve covered the necessary requirements to begin working with Keystone.js application framework. Onwards!

- 1800+ high-performance UI components.
- Includes popular controls such as Grid, Chart, Scheduler, and more.
- 24x5 unlimited support by developers.

