CHAPTER 4
Symmetric Encryption
Symmetric encryption is performed on streams and is useful when encrypting large amounts of data. A special stream class called CryptoStream is used to encrypt the data that is read into the stream.
Note: Symmetric encryption uses the same key for encrypting and decrypting data.
Streams that derive from the Stream class can be used with the CryptoStream class. The derived classes of the Stream class are:
- Microsoft.JScript.COMCharStream
- System.Data.OracleClient.OracleBFile
- System.Data.OracleClient.OracleLob
- System.Data.SqlTypes.SqlFileStream
- System.IO.BufferedStream
- System.IO.FileStream
- System.IO.MemoryStream
- System.IO.UnmanagedMemoryStream
- System.IO.Compression.DeflateStream
- System.IO.Compression.GZipStream
- System.IO.Pipes.PipeStream
- System.Net.Security.AuthenticatedStream
- System.Net.Sockets.NetworkStream
- System.Printing.PrintQueueStream
- System.Security.Cryptography.CryptoStream
To illustrate the use of symmetric encryption, we will read a large text file, encrypt the contents, and write it to an encrypted file.
Code Listing 23: Symmetric Encryption
public static void SymmetricEncryptionExample() { string path = @"c:\temp\war_and_peace.txt"; FileInfo fi = new FileInfo(path); string directory = fi.DirectoryName;
string textToEncrypt = ""; byte[] encryptedText;
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(path)) { textToEncrypt = sr.ReadToEnd(); } using (RijndaelManaged crypto = new RijndaelManaged()) { crypto.GenerateKey(); crypto.GenerateIV(); ICryptoTransform encrypt = crypto.CreateEncryptor(crypto.Key, crypto.IV);
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream()) { using (CryptoStream cryptStream = new CryptoStream(ms, encrypt, CryptoStreamMode.Write)) { using (StreamWriter writer = new StreamWriter(cryptStream)) { writer.Write(textToEncrypt); } encryptedText = ms.ToArray(); } using (FileStream fs = new FileStream(Path.Combine(directory, "war_and_peace_encrypted.txt"), FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write)) { fs.Write(encryptedText, 0, encryptedText.Length); } } } } |
In the first section of the SymmetricEncryptionExample() method, we’re not doing anything spectacular. We are simply opening a large text file and reading its contents into a string. We then create a RijndaelManaged object and generate a random symmetric algorithm key and a random initialization vector for the algorithm. We then create a Rijndael encryptor object for the key and initialization vector. Then we encrypt the text using a CryptoStream object.
Lastly, we write the encrypted text to a new file.
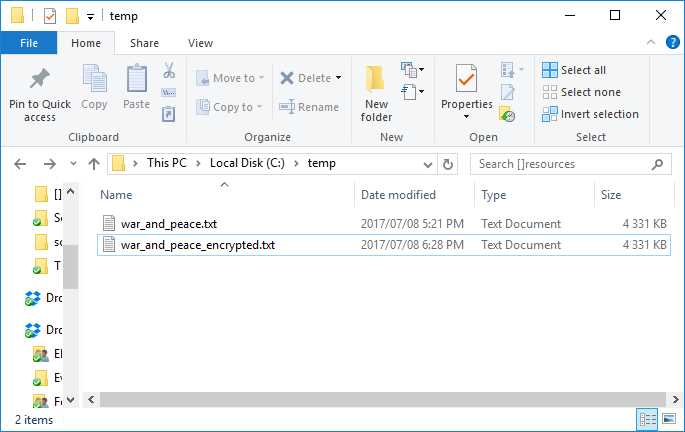
Figure 13: Encrypted File
If we have a look at the contents of the file, we can see that it has most definitely been encrypted.
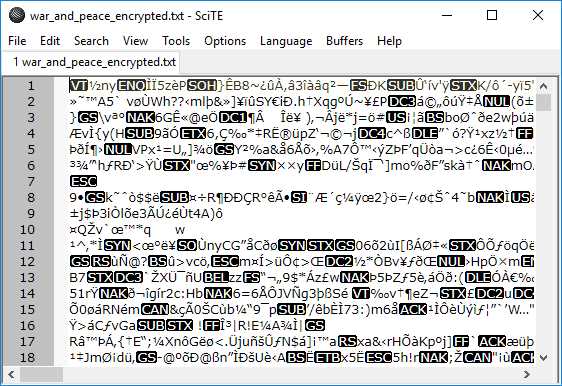
Figure 14: Encrypted File Contents
Decrypting the file back into plain text is also easy enough to do. We pass the method the encrypted text, the random symmetric algorithm key, and the random initialization vector for the algorithm. You will notice that this time the encrypted text is passed to the MemoryStream.
Code Listing 24: Decrypt the File
public static void DecryptFile(byte[] encryptedText, byte[] key, byte[] initVector, string directory) { string decryptedText; using (RijndaelManaged crypto = new RijndaelManaged()) { crypto.Key = key; crypto.IV = initVector; ICryptoTransform decrypt = crypto.CreateDecryptor(crypto.Key, crypto.IV); using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream(encryptedText)) { using (CryptoStream decryptStream = new CryptoStream(ms, decrypt, CryptoStreamMode.Read)) { using (StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(decryptStream)) { decryptedText = reader.ReadToEnd(); } } File.WriteAllText(Path.Combine(directory, "war_and_peace_decrypted.txt"), decryptedText); } } } |
We now also call the CreateDecryptor method on the RijndaelManaged object. The CryptoStream then decrypts the text and writes that to a file.
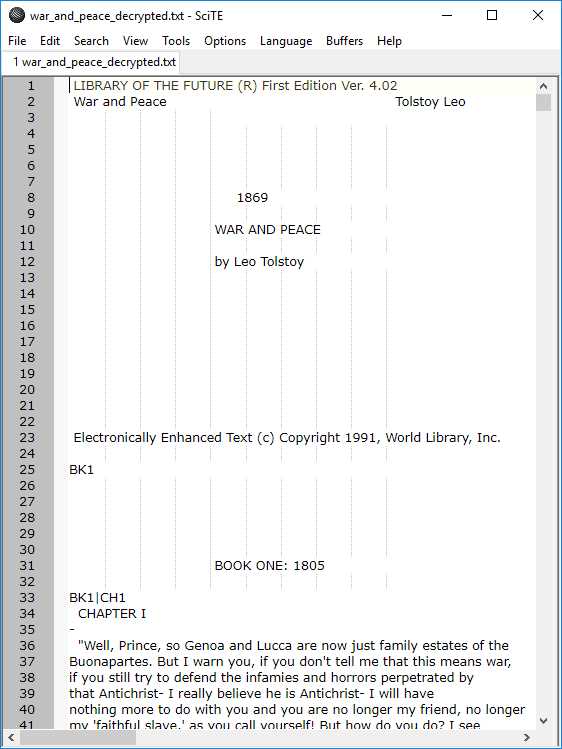
Figure 15: Decrypted File
As we can see, when the file is opened, it contains the decrypted text.
The generated key
When we called the crypto.GenerateKey() method on the RijndaelManaged object, we created a random byte array to store the encryption key. This key is used for both encryption and decryption of data.
The initialization vector
We also created an initialization vector by calling the crypto.GenerateIV() method on the RijndaelManaged object. It prevents data repetition and makes it difficult for hacking attempts to find patterns. A new random initialization vector is generated whenever the GenerateIV() method is called.

- 1800+ high-performance UI components.
- Includes popular controls such as Grid, Chart, Scheduler, and more.
- 24x5 unlimited support by developers.

