CHAPTER 5
Asymmetric Encryption
While symmetric encryption is performed on streams and is good for encrypting large amounts of data, asymmetric encryption is performed on small amounts of data. Imagine for a minute that you want to send me a secret message. How would you do that?
The following graphic summarizes the process of asymmetric encryption (also known as public key cryptography).
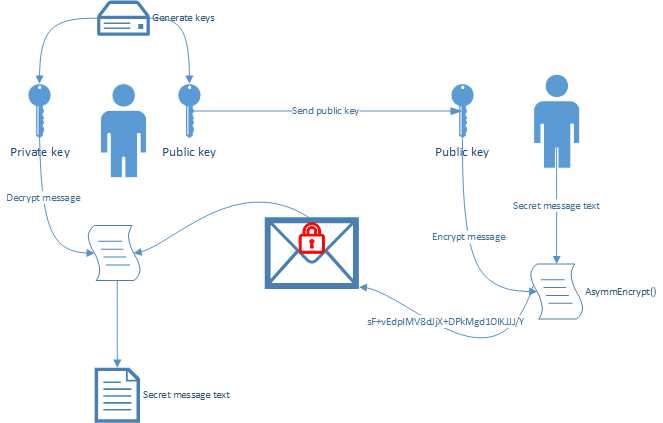
Figure 16: Asymmetric Encryption Summarized
You will see that the process starts on the left, where public and private keys are generated. You will also notice that the private key is never shared. Only the public key is shared between both parties.
Note: Asymmetric encryption uses mathematically linked public and private keys.
Let’s see how to implement asymmetric encryption in code.
Writing the code
First, I generate a public and a private key that I store either in memory or in a cryptographic key container.
Note: The public key is the Modulus and Exponent.
Generating the public key is done as seen in Code Listing 25.
Code Listing 25: Generate Public and Private Keys
Next, I will send you my public key. Using my public key, you encrypt the secret message and send the encrypted message back to me.
Code Listing 26: Encrypting the Message
byte[] toEncrypt = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes("Secret message text to encrypt"); byte[] encryptedData = AsymmEncrypt(toEncrypt, publicMod, publicExp); |
The AsymmEncrypt() method encrypts the data you want to send me. Note that this code will be running on your computer, in the application you encrypt the message with. It is included here (Code Listing 27) in the same application for illustration purposes.
Code Listing 27: Asymmetric Encryption Method
public static byte[] AsymmEncrypt(byte[] dataToEncrypt, byte[] mod, byte[] exp) { RSACryptoServiceProvider crypto = new RSACryptoServiceProvider(); RSAParameters RSAKeyInfo = new RSAParameters(); RSAKeyInfo.Modulus = mod; RSAKeyInfo.Exponent = exp; crypto.ImportParameters(RSAKeyInfo);
byte[] encryptedData;
//Encrypt the data encryptedData = crypto.Encrypt(dataToEncrypt, false);
return encryptedData; } |
After I receive the encrypted message from you, I decrypt it using the private key that corresponds to the public keys I sent you. I can only decrypt the message if I use the private key that corresponds to the public key you used to encrypt the secret message. If not, the decryption will fail.
Code Listing 28: Decrypt Secret Message
byte[] decrypted = rsaCrypto.Decrypt(encryptedData, false); string secretMessage = Encoding.Default.GetString(decrypted); |
If we look at the output of the console application, we can see that the message was successfully decrypted.
Figure 17: Decrypted Message
The message was encrypted and securely sent to me, where it was securely decrypted.

- 1800+ high-performance UI components.
- Includes popular controls such as Grid, Chart, Scheduler, and more.
- 24x5 unlimited support by developers.

