TL;DR: Stop relying on static address inputs! This guide shows how to build a seamless, real-time location search using Google Places API and Syncfusion’s Blazor AutoComplete component. Learn how to fetch live suggestions, display interactive maps, and handle user selections with JavaScript interop. Perfect for apps in delivery, real estate, and travel, this solution boosts UX, accuracy, and engagement.
Looking to add a sleek, real-time location search to your Blazor app? Whether you’re building a delivery platform, a travel planner, or a real estate listing site, users expect fast, accurate, and interactive address suggestions.
In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to integrate the Google Places API with Syncfusion’s Blazor AutoComplete component to create a seamless location search experience. From fetching live suggestions to rendering interactive maps, you’ll learn how to build a feature that’s not only functional but also delightful to use.
Prerequisites
Before implementing this solution, ensure you have the following:
- A Google cloud project with Places API enabled
- Get an API key from the Google Cloud Console.
- Enable the Places API for your project.
- System requirements
- Basic knowledge of JavaScript Interop in Blazor
- Understanding IJSRuntime is necessary, since we’ll be calling google maps JavaScript APIs from Blazor.
Implementation steps
Step 1: Set up the Blazor project
Start by creating a new Blazor Server or Blazor WebAssembly project in Visual Studio. For more information, refer to Getting started with Syncfusion® Blazor Web App in Visual Studio for guidance.
Step 2: Add google maps API script
To enable Google Maps and Places API functionality, include the google maps JavaScript API script with the Places library in your App.razor file. Replace YOUR-API-KEY-GOES-HERE with your actual API key obtained from the google cloud console.
<script src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?key=YOUR-API-KEY-GOES-HERE&libraries=places"></script>
This script loads the necessary Google Maps APIs, enabling location predictions and map rendering in your Blazor application.
Step 3: Configure the Blazor AutoComplete component
AutoComplete component setup
The AutoComplete component is defined in the razor page to capture user input and display location suggestions.
Here’s the complete markup code example.
<SfAutoComplete ID="Places_Element" @ref="AutoCompleteObj" TValue="string" TItem="PredictionResult" Placeholder="Enter Location" FloatLabelType="Syncfusion.Blazor.Inputs.FloatLabelType.Auto" AllowCustom="false">
<AutoCompleteTemplates TItem="PredictionResult">
<NoRecordsTemplate>
<span class='norecord'> Enter a valid value to search for the address </span>
</NoRecordsTemplate>
</AutoCompleteTemplates>
<AutoCompleteFieldSettings Value="Description"></AutoCompleteFieldSettings>
<AutoCompleteEvents TValue="string" TItem="PredictionResult" Created="@RenderMap" Filtering="@OnFiltering" ValueChange="@ChangeHandler"></AutoCompleteEvents>
</SfAutoComplete>-
ID and @ref: The
ID="Places_Element"uniquely identifies the component, while@ref="AutoCompleteObj"creates a reference to the component instance for programmatic control in C# code. - TValue and TItem:
TValue="string"specifies that the selected value is a string (the location description), whileTItem="PredictionResult"defines the data model for suggestions (explained in section 3.2). - AllowCustom=”false”: Prevents users from entering values not provided by the API, ensuring valid addresses.
- Templates: The
<NoRecordsTemplate>displays a custom message when no suggestions are found, improving user feedback. - Field settings:
<AutoCompleteFieldSettings Value="Description">maps the description property of PredictionResult to the dropdown suggestions. - Events: The component handles three events:
- Created=
"@RenderMap": Initializes the map when the component is rendered. - Filtering=
"@OnFiltering": Triggers when the user types, fetching suggestions. - ValueChange=
"@ChangeHandler": Handles selection of a location to update the map.
- Created=
- Map container: The
<div id="map">below the AutoComplete provides a 400px-high area for rendering the google map.
PredictionResult class
To handle Google Places API responses, define a C# model that maps the JSON structure of location predictions. This model is used by the AutoComplete component to display suggestions.
public class PredictionResult
{
[JsonPropertyName("description")]
public string Description { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("placeId")]
public string PlaceId { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("matchedSubstrings")]
public List<MatchedSubstring> MatchedSubstrings { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("structuredFormatting")]
public StructuredFormatting StructuredFormatting { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("terms")]
public List<Term> Terms { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("types")]
public List<string> Types { get; set; }
}
public class MatchedSubstring
{
[JsonPropertyName("length")]
public int? Length { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("offset")]
public int? Offset { get; set; }
}
public class StructuredFormatting
{
[JsonPropertyName("main_text")]
public string MainText { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("main_text_matched_substrings")]
public List<MatchedSubstring> MainTextMatchedSubstrings { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("secondary_text")]
public string SecondaryText { get; set; }
}
public class Term
{
[JsonPropertyName("offset")]
public int? Offset { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("value")]
public string Value { get; set; }
}
Component code-behind
The C# code-behind manages the AutoComplete’s behavior and JavaScript interop. Here’s the code example with explanations.
[Inject]
protected IJSRuntime JsRuntime {get; set;}
public List<PredictionResult> filteredData {get; set;} = new List<PredictionResult>();
public SfAutoComplete<string, PredictionResult> AutoCompleteObj{ get; set;}
- IJSRuntime Injection: The JsRuntime property is injected to enable calling JavaScript functions from C#, necessary for interacting with Google Maps APIs.
- filteredData: A list to store API-fetched location predictions, used to populate the AutoComplete dropdown.
- AutoCompleteObj: A reference to the SfAutoComplete component, allowing to update the filtering results to the component.
Step 4: Handle AutoComplete events
The AutoComplete component responds to user interactions through events. Below are the event handlers with detailed explanations.
- Handle created event (RenderMap): The RenderMap method initializes the map when the AutoComplete component is first rendered.
private async Task RenderMap()
{
await JsRuntime.InvokeVoidAsync("initMap", string.Empty);
}
- Handle filtering (OnFiltering) event.
- Triggered as the user types.
- Calls OnFilter via JS Interop to fetch predictions.
- Updates the AutoComplete dropdown with results.
public async Task OnFiltering(FilteringEventArgs args)
{
filteredData.Clear();
args.PreventDefaultAction = true;
if (args.Text != "")
{
filteredData = await JsRuntime.InvokeAsync<List<PredictionResult>>("OnFilter", args.Text);
}
await AutoCompleteObj.FilterAsync(filteredData, new Query());
}
- Handle ValueChange (ChangeHandler) Event: When a user selects a location, the PlaceId is passed to initMap to display the location on the map.
public async Task ChangeHandler(ChangeEventArgs<string, PredictionResult> args)
{
var placeId = (args.ItemData != null && args.ItemData.PlaceId != null && args.ItemData.PlaceId != string.Empty)
? args.ItemData.PlaceId
: string.Empty;
await JsRuntime.InvokeVoidAsync("initMap", placeId);
}
Step 5. Implement JavaScript interop for google maps
Two key JavaScript functions used:
- OnFilter – Fetches location predictions from Google Places API.
- Uses google.maps.places.AutocompleteService to fetch location predictions.
- Returns structured data to Blazor.
window.OnFilter = function (text) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const service = new google.maps.places.AutocompleteService();
service.getQueryPredictions({ input: text }, function (predictions, status) {
if (status === google.maps.places.PlacesServiceStatus.OK) {
resolve(predictions.map(p => ({
description: p.description,
placeId: p.place_id,
matchedSubstrings: p.matched_substrings || [],
structuredFormatting: p.structured_formatting || {},
terms: p.terms || [],
types: p.types || []
})));
} else {
resolve([]);
}
});
});
};
- initMap – Initializes and updates the map based on the selected location.
- Initializes google maps if not already loaded.
- If a placeId is provided, it fetches details (like coordinates) and displays a marker.
var map;
var markers = [];
function initMap(placeId) {
if (map === undefined || map === null) {
map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map"), {
center: { lat: 35.855398, lng: -78.815522 },
zoom: 5,
});
}
markers.forEach(marker => marker.setMap(null));
markers = [];
if (placeId && placeId !== "") {
const request = {
placeId: placeId,
fields: ["geometry", "name"]
};
const service = new google.maps.places.PlacesService(map);
service.getDetails(request, (place, status) => {
if (status === google.maps.places.PlacesServiceStatus.OK) {
if (place.geometry) {
map.setCenter(place.geometry.location);
map.setZoom(15);
const marker = new google.maps.Marker({
map: map,
position: place.geometry.location,
title: place.name,
animation: google.maps.Animation.BOUNCE
});
markers.push(marker);
} else {
console.error("Place has no geometry.");
}
} else {
console.error("Place details request failed due to " + status);
}
});
}
}
How it all works together
1. User types in AutoComplete:
- The OnFiltering event triggers, calling OnFilter in JavaScript.
- Google Places API returns matching locations, which are displayed in the popup.
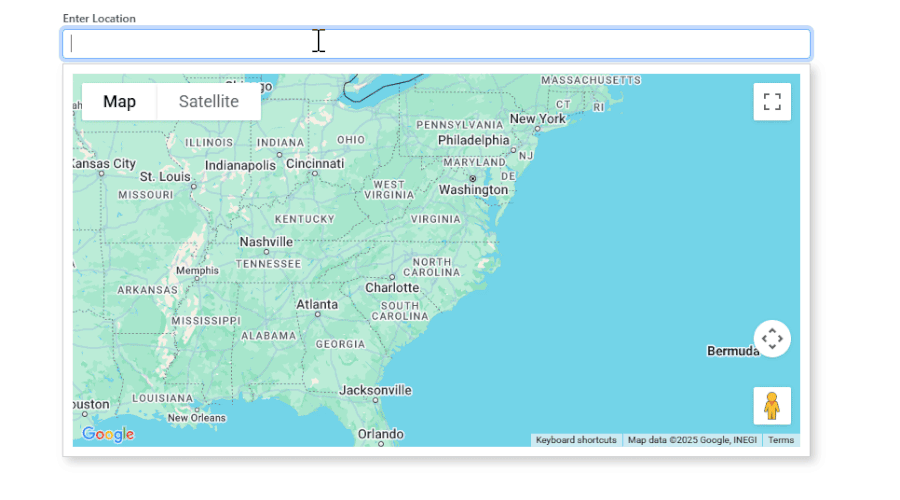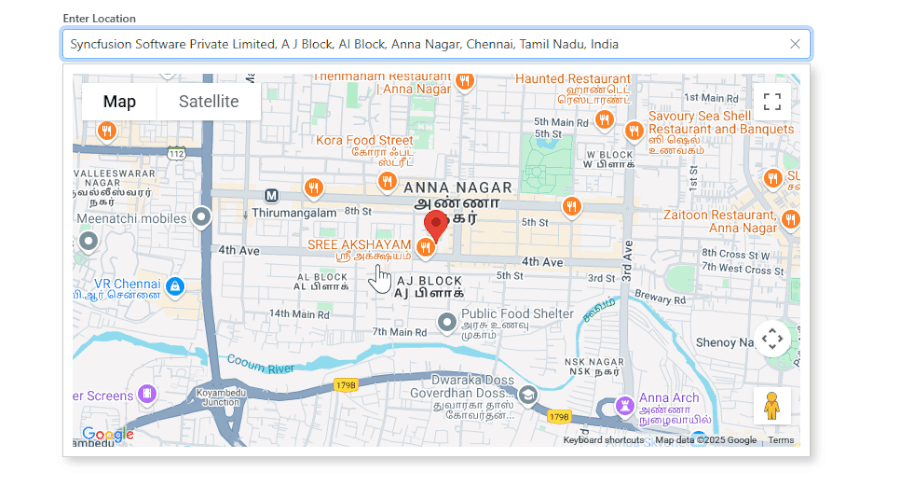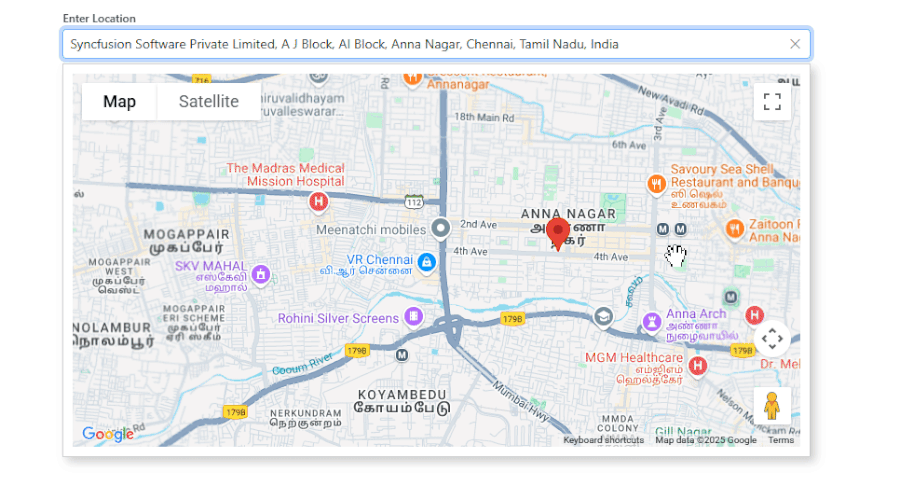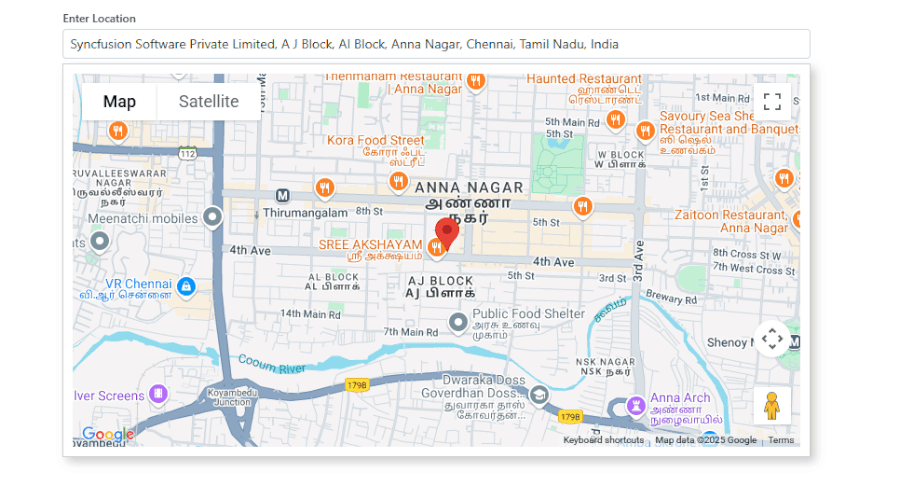
2. User selects a location:
- The ValueChange event passes the PlaceId to initMap.
- Google Maps centers on the selected location and adds a marker.
3. Live interactive map:
- The map dynamically updates whenever a new location is selected.
FAQs
Q1: How do I bind a list of items to the Blazor AutoComplete component?
You can bind a list of values to the AutoComplete component using its DataSource property. This allows you to display a set of options from which users can choose.
Q2: How can I control the minimum number of characters before suggestions appear?
The MinLength property allows you to specify the minimum number of characters a user must type before the AutoComplete component starts displaying suggestions.
Q3: How do I enable highlighting of the matching text in suggestions?
You can enable the highlighting feature by setting the Highlight property to true. This will visually emphasize the text in the suggestions that matches the user’s input.
Q4: How do I handle events when a user selects a value from the AutoComplete list?
The AutoComplete component provides various events such as OnValueSelect that you can use to execute custom logic whenever a selection is made. You can attach event handlers to manage actions like displaying additional information, triggering other changes in the UI, or updating data based on the selected value.

Syncfusion Blazor components can be transformed into stunning and efficient web apps.
Conclusion
Thanks for following along! By combining the power of Google Places API with Blazor AutoComplete, you’ve now got a robust, real-time location search feature that enhances user experience and adds serious value to your app.
Whether you’re building for e-commerce deliveries, travel bookings, real estate listings, or ride-hailing platforms, this integration ensures your users can find and select locations quickly and accurately.
If you’re an existing Syncfusion® user, you can download the latest version of Essential Studio® from the License and Downloads page. For those new to Syncfusion®, we offer a 30-day free trial so you can experience these exciting features firsthand.
Need help? Feel free to reach out via our support forum, support portal, or feedback portal. We’re always here to assist you!