TL;DR: Looking to speed up React apps without adding more client-side code? Explore how HTMX delivers dynamic server-rendered HTML updates in React and Next.js, resulting in cleaner components and smoother performance.
React gives you a powerful foundation for building interactive, component-driven applications. Its virtual DOM, tooling ecosystem, and predictable component architecture make it a go-to choice for modern front-end development. However, as your app grows, client-side rendering can lead to larger JavaScript bundles and more complex state management than you actually need.
That’s where HTMX fits in. HTMX is a lightweight library that lets you update parts of the UI using simple HTML attributes instead of additional client-side JavaScript. When you combine HTMX with React and Next.js, you get a fast, flexible setup that delivers SEO‑friendly, server-driven UI updates without sacrificing component structure or developer experience.
In this guide, we’ll walk through how to integrate HTMX into a Next.js project to streamline dynamic updates, reduce JavaScript overhead, and keep your UI performant.

Syncfusion React UI components are the developers’ choice to build user-friendly web applications. You deserve them too.
What is HTMX?
HTMX is a compact JavaScript library (~14KB) that brings dynamic functionality like AJAX, WebSockets, and CSS transitions, directly to HTML via declarative attributes. Instead of writing JavaScript for every interaction, you can add attributes like hx-get to trigger server requests and update the DOM.
Code example to achieve this:
<button
hx-get="/api/content"
hx-target="#output"
hx-swap="innerHTML">
Load Data
</button>
<div id="output"></div>The key benefits of HTMX include,
- Server-driven updates: Fetch and inject HTML snippets from the server into specific DOM elements.
- Minimal JavaScript: Replace complex client-side logic with declarative attributes.
- Fast and lightweight: Avoid full page reloads for snappy, responsive UIs.
- SEO-friendly: Server-rendered HTML is easily crawlable by search engines.
Why combine HTMX with React and Next.js?
Next.js, paired with React 19, offers powerful features like server components, streaming, and improved hydration, making it ideal for modern web apps. HTMX complements this setup by:
- Simplifying dynamic updates: Fetch server-rendered HTML for content-heavy sections like dashboards or forms.
- Reducing JavaScript overhead: Minimize client-side rendering to boost performance and reduce bundle size.
- Enhancing SEO: Deliver crawler-friendly HTML for content-driven pages like blogs or e-commerce listings.
- Streamlining development: Combine React’s component model with HTMX’s simplicity for faster iteration.
This hybrid approach is particularly effective on interfaces where server-side rendering or partial updates outperform client-side rendering, such as data grids, search results, or real-time dashboards.
Setting up HTMX in a Next.js (React 19) app
You can integrate HTMX into any Next.js project with just a few steps. If you’re familiar with React and the Next.js App Router, you’ll find the workflow straightforward.
Prerequisites
Before you get started, make sure your environment meets the following requirements:
- Node.js: Version 20.0.0 or higher.
- Package manager: npm, pnpm, or yarn.
- Next.js: Version 15.1 or later (for full React 19 support).
- React/React-DOM: Version 19 (stable).
- Text editor: VSCode or similar, plus a terminal.
Once you have these in place, you’re ready to create the project.

A to Z about Syncfusion’s versatile React components and their feature set.
Step 1: Create a Next.js project
Start by creating a new Next.js project with TypeScript and the App Router. These options ensure compatibility with React 19, modern routing patterns, server components, and future-friendly development practices.
Run the following command in your terminal:
npx create-next-app@latest my-htmx-app --typescript --appOnce the project is created, navigate to the project folder and install dependencies:
cd my-htmx-app && npm installStep 2: Add HTMX to Next.js layout
Include HTMX via a CDN in the root layout app/layout.tsx to ensure it loads early:
import Script from 'next/script';
export default function RootLayout({ children }: { children: React.ReactNode })
{return
( <html lang="en">
<head>
<Script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]" />
<Script src="https://unpkg.com/[email protected]/dist/ext/sse.js" />
</head>
<body>{children}</body>
</html>
);
}Step 3: Create a server endpoint for HTMX
Next, you need to set up an API route to serve HTML snippets for HTMX requests, as shown in the code below:
import { NextResponse } from 'next/server';
export async function GET()
{ return new NextResponse
('<p class="text-green-600">Content loaded via HTMX!</p>',
{
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'text/html' },
}
);
}This endpoint returns a styled HTML snippet that HTMX can inject into the page.
Step 4: Integrate HTMX in a React component
Then, create a page app/page.tsx with a React component that uses HTMX for dynamic updates:
'use client';
import { useEffect } from 'react';
declare global
{ interface Window
{ // eslint-disable-next-line @typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any
htmx?: any;
}
}
export default function Home()
{ useEffect(() =>
{ if (typeof window !== 'undefined' && window.htmx)
{ window.htmx.process(document.querySelector('#htmx-container'));
}
}, []);
return
( <div id="htmx-container" data-hx-preserve className="p-6 max-w-md mx-auto">
<button
className="bg-blue-500 text-white px-4 py-2 rounded hover:bg-blue-600 transition"
hx-get="/api/message"
hx-target="#output"
hx-swap="innerHTML"
>
Load Content
</button>
<div id="output" className="mt-4 text-lg"></div>
</div>
);
}Let’s understand how it works:
- HTMX initialization: The
useEffecthook processes the#htmx-containerelement to enable HTMX functionality. - Preserving DOM: The
data-hx-preserveattribute prevents React from overwriting HTMX-managed DOM sections. - Dynamic updates: Clicking the button triggers an
hx-getrequest to/api/message, injecting the response into the `#output` div. - Styling: Tailwind CSS ensures a polished, responsive UI.
As a result, a single button click updates the page with server-rendered content, keeping the UI fast and lightweight.
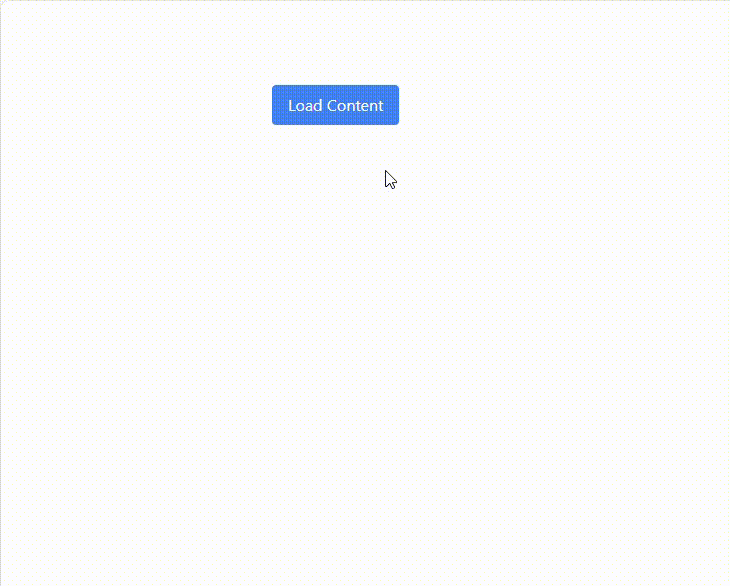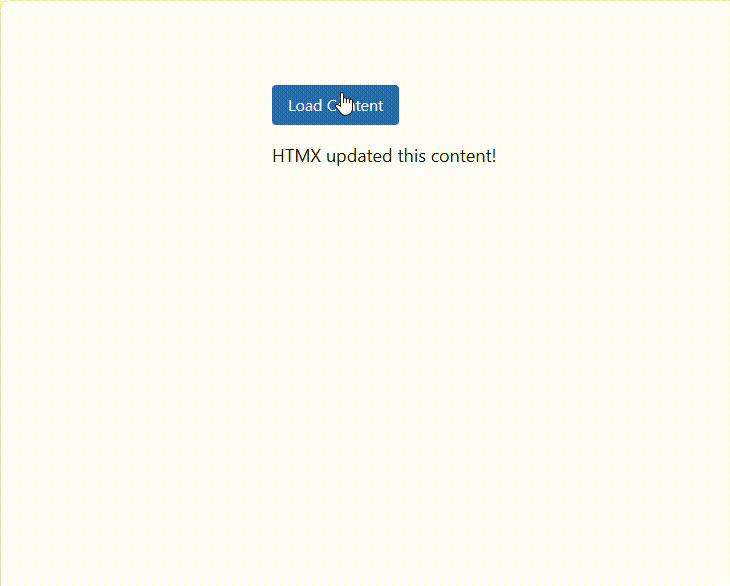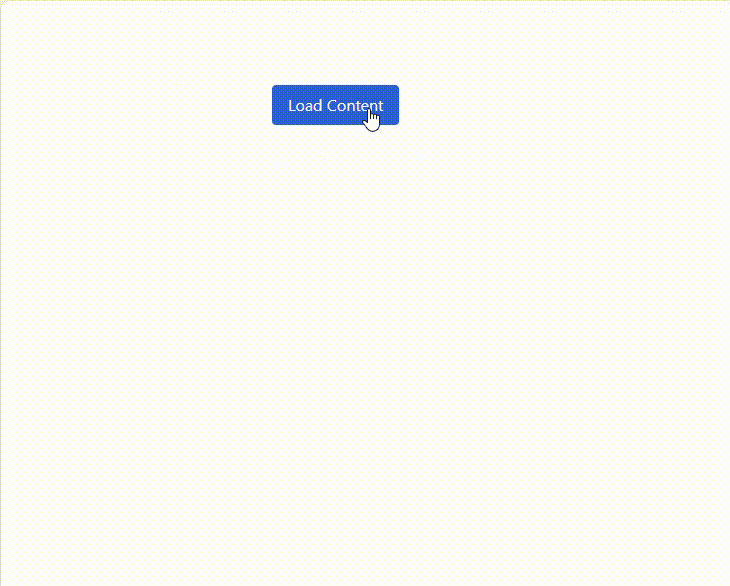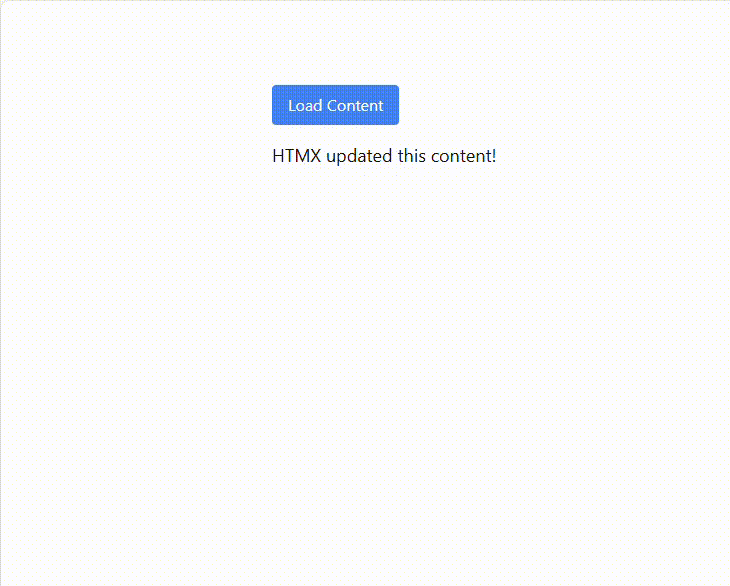

See the possibilities for yourself with live demos of Syncfusion React components.
Tips for using HTMX with React
Here are some best practices to help you use HTMX effectively alongside React:
- Isolate HTMX logic: Use
data-hx-preserveon HTMX-managed DOM sections to prevent React from overwriting them. - Prevent event conflicts: Use
e.stopPropagation()ande.preventDefault()to avoid clashes between HTMX and React event handlers. - Optimize server responses: Return minimal HTML snippets to reduce latency and improve performance.
- Leverage Tailwind CSS: Style components consistently for a professional, responsive UI.
- Monitor DOM changes: Use
MutationObserverfor dynamic components like grids to ensure HTMX processes new elements. - SEO test: Verify that server-rendered HTML is crawler-friendly using tools like Google’s Lighthouse.
When to use HTMX in React
HTMX shines in scenarios where server-driven updates simplify development or improve performance:
- Content-heavy pages: Blogs, news feeds, or search results benefit from server-rendered HTML.
- SEO-critical apps: E-commerce or marketing sites needing crawler-friendly content.
- Simple interactions: Forms, notifications, or modals that don’t require complex React state.
- Hybrid apps: Combine React’s interactivity for dynamic UIs with HTMX for lightweight updates.
GitHub reference
For more details about integrating HTMX with React and Next.js, refer to the GitHub demo.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why integrate HTMX with Syncfusion React components?
Syncfusion gives rich, complex widgets (grids, charts, etc.). HTMX adds fast, low-JS server HTML updates for simple parts → better speed, smaller bundles.
How do you combine HTMX and Syncfusion React components effectively?
Use Syncfusion for heavy interactive controls. Apply HTMX attributes to surrounding HTML or non-Syncfusion areas. Target swaps outside React roots or embed triggers carefully. Load HTMX once globally and avoid event conflicts.
When does React + HTMX + Syncfusion make more sense than pure React/Syncfusion?
Choose hybrid for ultra-fast CRUD/filters, server-rendered HTML, mobile speed, and minimal JS. Use pure React/Syncfusion for deep client-side state or full SPA apps.
What performance gains can you expect with HTMX in Syncfusion React apps?
50–300 ms faster partial updates (raw HTML vs JSON + re-render). Smaller bundles. Lightning-fast feel on lists, forms, dashboards, especially with heavy Syncfusion components.

Explore the endless possibilities with Syncfusion’s outstanding React UI components.
Conclusion
Thank you for reading! Pairing HTMX with React and Next.js gives you a balanced, developer-friendly approach to building modern web apps. You keep React’s component structure while offloading dynamic updates to lightweight server-driven HTML. The result is a fast, SEO‑friendly, maintainable UI with less JavaScript and fewer moving parts. Whether you’re updating a small component or enhancing a complex grid, HTMX helps you keep your codebase efficient and responsive.
Try out the steps in your own Next.js project and let us know how it goes in the comments section. You can contact us through our feedback portal. We are always happy to assist you!




